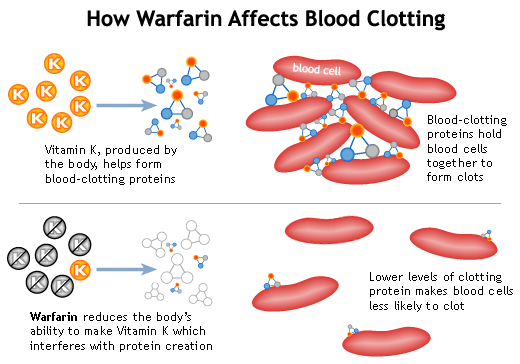
Coumadin or Warfarin is an anticoagulant or a “blood thinner”. Coumadin slows the normal clotting process by blocking the activity of vitamin K. Vitamin K is needed to produce 4 clotting proteins, thus Coumadin reduces the amount of clotting proteins. It “thins your blood” to prevent blood clots from forming. But when a clot is formed, it does not dissolve clots. Coumadin prevents extension of existing clots or the formation of new clots, when used at the appropriate levels.
There are several medical conditions that warrant the Use of Coumadin: A pulmonary emboli (a blood clot in the lung), deep vein thrombosis (a blood clot deep in the vein, usually in the legs), atrial fibrillation (an irregular heart rhythm that cause the heart to pump blood out at irregular intervals) and others.
There is a highly variable response from patient to patient to achieve the Therapeutic range or “thinning the blood”. Coumadin effect builds slowly over one week or more to see maximal effect. There is no standard way to estimate the dose needed, thus it requires frequent blood test (PT/INR). Take only the doses prescribed by your doctor. The Doses may change based on the blood test results. Use a calendar, pillbox, or some other way to keep track and have blood tests as instructed.
This is why your doctor will want you to have your blood drawn regularly to check the PT/INR. The PT/INR results will tell your doctor how long it takes for your blood to clot and adjust your Coumadin dosage accordingly. For new patients, the INR should be measured 1or 2 times weekly. When the INRs are consistent & stable, it can be done weekly or every other week, but no less frequent than every 4 weeks for stable patients. It is very important to follow your doctor’s orders concerning the blood work and dosage changes.
When you are taking Coumadin, there are some important things to remember. You should avoid an excessive diet of foods that are high in Vitamin K, such as green leafy vegetables, broccoli, green onions, asparagus and olive oil. Also avoid Brussels sprouts, cabbage, collard greens, endive, green scallion, kale, spinach, turnip greens, watercress Salad Oils canola, and soybean oils mayonnaise Liver. Don’t change your diet when starting warfarin. Try to maintain consistency and be aware of foods high in vitamin K. Limit portion size of high vitamin K foods.
Coumadin and Vitamin K work against each other. Vitamin K actually helps thicken the blood. It is given to patients when someone’s blood is dangerously thin (Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin). Vitamin K lowers INR by making more clotting factors and Warfarin blocks the action of vitamin K and increases the INR).
You should also avoid dangerous or hazardous activities which could result in bleeding or fractures. You should use a soft bristle toothbrush when brushing your teeth. Carry a card with you at all times that states that you are on Coumadin. Be aware of any signs of abnormal bleeding and report them to your doctor immediately. Let all of your physicians know that you are on Coumadin. You should stop taking Coumadin prior to any surgical procedures. Up to 5 days are needed to achieve an INR less than 1.5 as a general rule before any surgery or procedures.
INR Target Range is where therapeutic effect is maximized and the benefit of clot prevention is achieved. Also the side effects are minimized with less chance of bleeding & bruising. The INR range depends upon the indication for therapy: An INR of 2.0 – 3.0 is needed For Stroke prevention, in persons with AFib or AFlut, DVT/PE treatment and Hip or knee replacement. An INR of 2.5 – 3.5 is needed for some mechanical heart valves and some hypercoagulable conditions (genetics), or people who have developed clots at lower INRs.
Coumadin should be taken every day at the same time. Usually, it is in the evening hours. If you miss a dose and it is still dark outside, take it when you remember. If the sun is up the next morning, skip it and Record the date and do not forget to inform your provider at the next INR measured. If your INR is too high, you may need less warfarin or if your INR is too low, you may need more warfarin but only with the guidance of your doctor. Do not change your Coumadin dose without your doctor instructions.
What are the risks of taking Coumadin? The main risk is that your blood may become too thin and cause you to bleed. Report unusual bleeding or Blood in stool (black, tarry color), Blood in urine (brown, red/pink color), Excessive nose bleeds/bleeding gums, Persistent oozing from superficial injuries, Excessive menstrual bleeding or unusual bruising (large areas), Sudden severe headache, Lightheadedness or fainting(intracranial bleed), Severe abdominal or back pain(intraabdominal bleed) . These are all Signs of Warfarin Excess and require immediate treatment. Avoid pregnancy and use a safe method of contraception while on Coumadin therapy. Coumadin use is contraindicated during pregnancy.
There are medicines that can interfere with Coumadin, and alter its effect. It is known as Drug interactions. Starting a new drug or stopping an old drug should be discussed with your doctor. Even herbal medicines and antibiotics can have this effect. Medications to Avoid include: NSAIDs (Aleve, Advil, Ibuprofen, Naproxen) Aspirin (unless prescribed by doctor) as they increase the risk of stomach bleeding (Vomiting blood or coffee ground material). Always check with your pharmacist or doctor before starting a non-prescription drug.
In Summary: Warfarin is a unique medication that requires patient education for its safe use. Use handouts in combination with verbal instructions. Properly educated patients should understand the need for INR testing and recognize adverse effects and know what to do.
The content of this website is provided for general informational purposes only and is not intended as, nor should it be considered a substitute for, professional medical advice. Do not use the information on this website for diagnosing or treating any medical or health condition. If you have or suspect you have a medical problem, promptly contact your professional healthcare provider.
